DualTKB: A Dual Learning Bridge between Text and Knowledge Base at EMNLP'20
DualTKB Presentation at EMNLP’20!
This work will be presented at the EMNLP’20 Gather Session 5D “Information Extraction” on 11/18/2020 at 1pm (UTC-5) US East Coast Time
DualTKB (very short) Introduction
DualTKB is a dual learning approach for unsupervised path-to-text and text-to-path transfer.
This bi-directional transfer us reframed as a translation task where we can use use translation cycles for consistency, by primarily to handle unsupervised training.
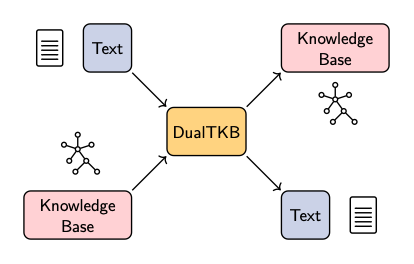
Our model is a simple encoder decoder architecture where the encoder is shared, while the decoders are specialized:
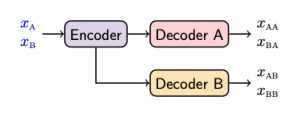 {}
{}
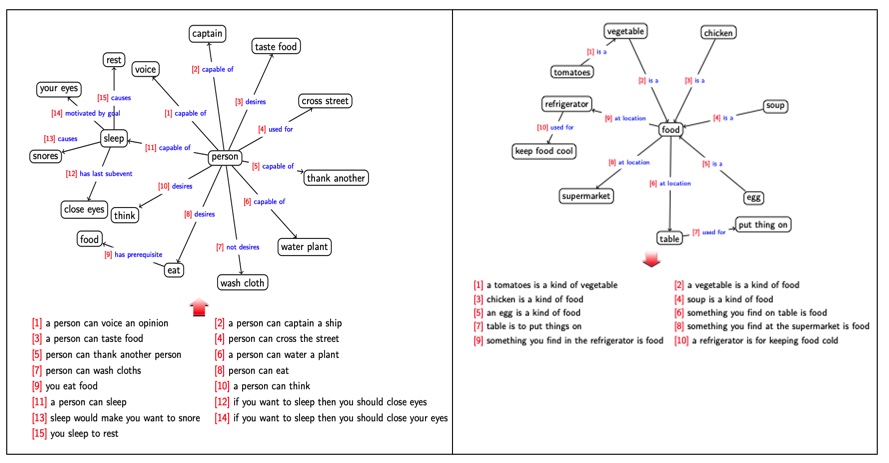
DualTKB at work:
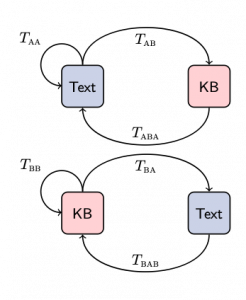
The training process is split into a translation stage followed by a back-translation stage. Inherently, the model can natively deal with both supervised and unsupervised data.
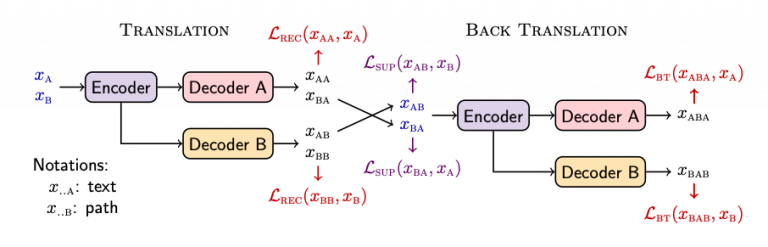
During the training we minimize a total loss:
\[\begin{align*} \mathcal{L} = \mathcal{L}_{\text{REC}} + \mathcal{L}_{\text{BT}} + \mathcal{L}_{\text{SUP}} \end{align*}\]where the reconstruction loss \(\mathcal{L}_\text{REC}\) controls the quality of the autoencoding process:
\[\begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{REC}} = \underset{x_{\text{A}} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_{\text{AA}}(x_{\text{A}})\right] + \underset{x_{\text{B}} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_{\text{BB}}(x_{\text{B}})\right], \end{align*}\]In a supervised training, the supervised loss \(\mathcal{L}_\text{SUP}\) is included to measure the cross-modality transfer:
\[\begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{SUP}} &= \underset{x_\text{A}, x_\text{B} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_\text{AB}(x_\text{B}|x_\text{A})\right] +\underset{x_\text{A}, x_\text{B} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_\text{BA}(x_\text{A}|x_\text{B})\right]. \end{align*}\]Finally, for unsupervised training (or weakly supervised training), we include a back-translation loss \(\mathcal{L}_{\text{BT}}\) whose purpose is to ensure that when the transferred modality (text or path) is back-translated into the original domain, the result matches the original input:
\[\begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{BT}} = \underset{x_\text{A} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_{\text{ABA}}(x_\text{A}| x_\text{AB})\right] +\underset{x_\text{B} \sim X}{\mathbb{E}}\left[-\log p_{\text{BAB}}(x_\text{B}|x_\text{BA})\right]. \end{align*}\]A DualTKB short description can be found on the companion IBM DualTKB website,
where, we will provide code, information about dataset, etc. over the next weeks.
For more in depth description, a version of our EMNLP’20 paper is available on arXiv.
Here are some examples of DualTKB transfering text-to-paths and path-to-text: